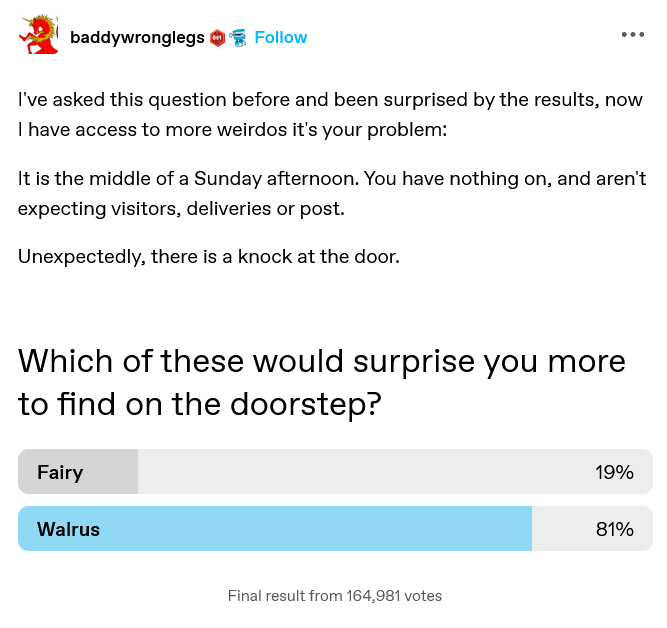
There’s been a thing going on in the past month on the Internet about fairies and walruses. If you’re not in the loop, it all started with a poll posted on tumblr by user baddywronglegs that asked respondents to consider which one they would be more surprised to find at their front door, a fairy or a walrus?
The fun of this poll is that it pits two very surprising (in most parts of the world) things against one another, but those things are surprising in two different ways. Fairies don’t exist, but if they did, it would be perfectly plausible for one to knock on your door. Walruses do exist, but the idea that one would survive the trip out of the Arctic, make it to your front door, and knock is beyond belief. What’s more surprising: the most unsurprising surprising thing or the most surprising unsurprising thing?
But, then, surprising things do happen sometimes. Like walruses showing up where they have no business being. A lost walrus found itself on the shores of southeastern Finland in the summer of 2022. It didn’t knock on any doors, but it did take a nap between some beached rowing boats, literally rolled around on someone’s yard in the grass, and posed in front of an emergency vehicle.
Yes, Finland is an Arctic country in the sense that we straddle the Arctic Circle, even though most of our land area is south of it. We do not, however, currently have any coastline in the north; all of our salt water access is to the south and west, i.e., to the Baltic Sea. Visits like this are, therefore, extremely rare. The walrus had to travel all the way around Scandinavia, through the Danish Straits (Kattegat and Skagerrak), and east along the Gulf of Finland to reach Hamina and Kotka.
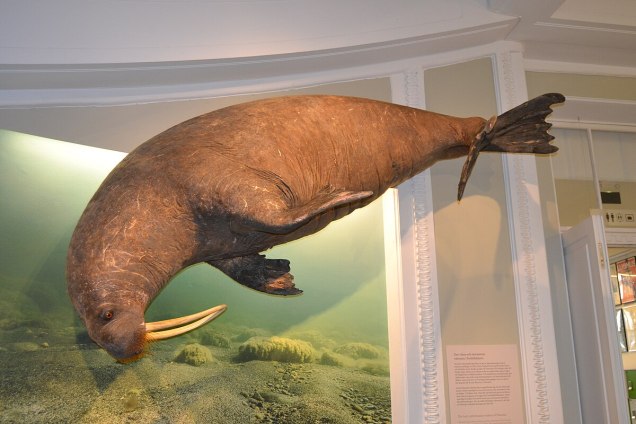
(Alas, the poor thing turned out to be famished, and died in the middle of an attempted rescue en route to the Wildlife Hospital of Korkeasaari Zoo in Helsinki. It’s since been preserved and it’s on display at the Finnish Museum of Natural History.)
It’s quite staggering that we live in a place where, theoretically—very much in theory, but nevertheless—a walrus could turn up on the yard! (No sign of fairies, though.)
Images: Screenshot of tumblr post by baddywronglegs. Stuffed walrus in the Natural History Museum of Helsinki by Antti Leppänen via Wikimedia (CC BY 4.0).
Out There highlights intriguing art, places, phenomena, flora, and fauna.
















You must be logged in to post a comment.